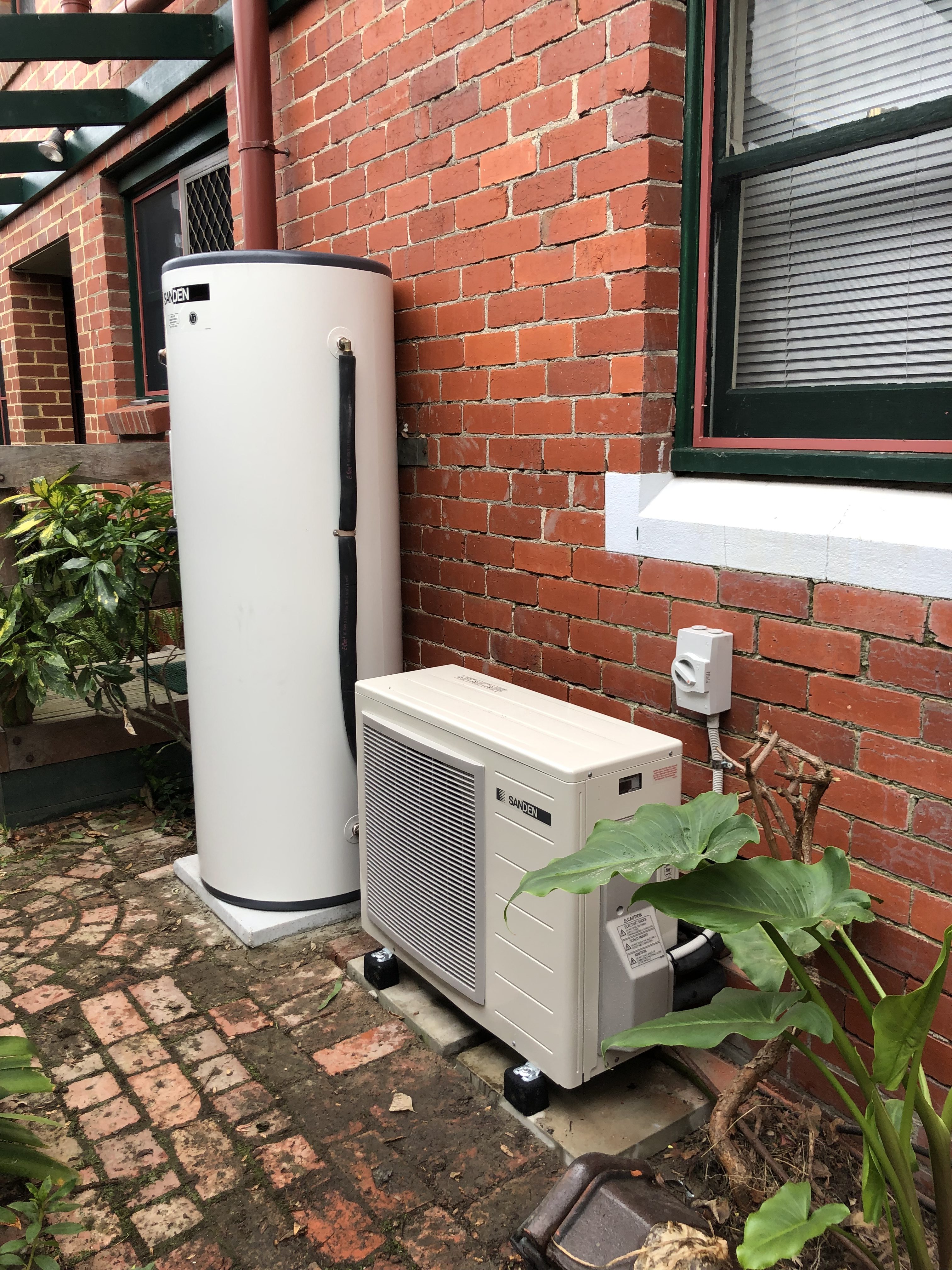
Whether you’re looking to lower your energy bill or keep your house at a comfortable temperature all year round, a heat pump system is worth exploring. Heat pumps are machines that move heat from one place to another.
Heat pumps can be used in both residential and commercial settings. How does a heat pump work? Let’s take a closer look.
Fundamentals of Heat Pumps
When attempting to provide a response to the query, “How do heat pumps work?” one of the most essential points to comprehend is that heating systems do not produce heat; rather, they transfer heat from one location to another.
In contrast to a furnace, which generates heat that is then dispersed throughout a residence, a heat pump pulls heat energy from the air outside the building (even when it is freezing outside) and converts it to the air within the building.
Both a heat pump and an air conditioning system are essentially equivalent while operating in the cooling mode since both draw heat from the air within the home and then discharge it through the exterior unit.
When deciding which sort of system would be most beneficial for your home, it is vital to take into account a number of important aspects, such as the size of your house and the climate in your area.
A local service provider has the knowledge and experience to correctly assess your unique requirements and guide you in making the best choice possible.
Heat Pumps and Their Crucial Parts
An outdoor unit, similar in appearance to the exhaust system of a split-system air conditioner, and an inside air handler unit are the two main components of a air source heat pump system. Components of equal importance can be found in both exterior and interior units.
Housing Unit
The inside unit, also known as the air handler unit, has a coil and a fan just like the outdoor unit.
While in cooling mode, the coil performs the role of an evaporator (in heating mode). The home’s ductwork and the coil depend on the fan to circulate air.
Exterior System
A fan and a coil are housed in the external device. Condenser (when cooling) or evaporator (when heating) depending on the mode the coil is in. The coil is exposed to the outside air, which is then heated by the fan.
Compressor
The refrigerant is pressurised by the compressor and distributed by it.
Refrigerant
The heat pump’s refrigerant is the fluid responsible for taking in and giving off heat.
Limiting Valve
When the expansion valve is open, the temperature and the pressure of the refrigerant are lowered because the flow of the refrigerant is controlled.
Balance Changer
The component of a heat pump is responsible for switching its operation from cooling to heating by reversing the flow of refrigerant.
The Function and Nature of Heat Pumps
Heat pumps have been widely utilised for decades to offer cost-effective heating, cooling, and even domestic hot water in a variety of locations around the world, including Australia.
Nature of Heat Pumps
Among the most fundamental principles of heat pump functioning and heat transfer is that hotter, denser locations will always want to shift heat energy to cooler, less pressurised ones. Heat pumps depend on this aspect of physics to transfer heat from one place to another by bringing warm air into contact with colder, reduced air. A heat pump operates in this way.
There are three distinct phases in an air-source heat pump’s operation:
- Heating: Heat is supplied to the structure through a cycle called the heating cycle.
- Cooling: Process of removing heat from a structure (the cooling cycle).
- Defrosting: During the defrost cycle, outdoor coils are defrosted to prevent ice buildup.
How Heat Pumps Work: A Step-by-Step Process
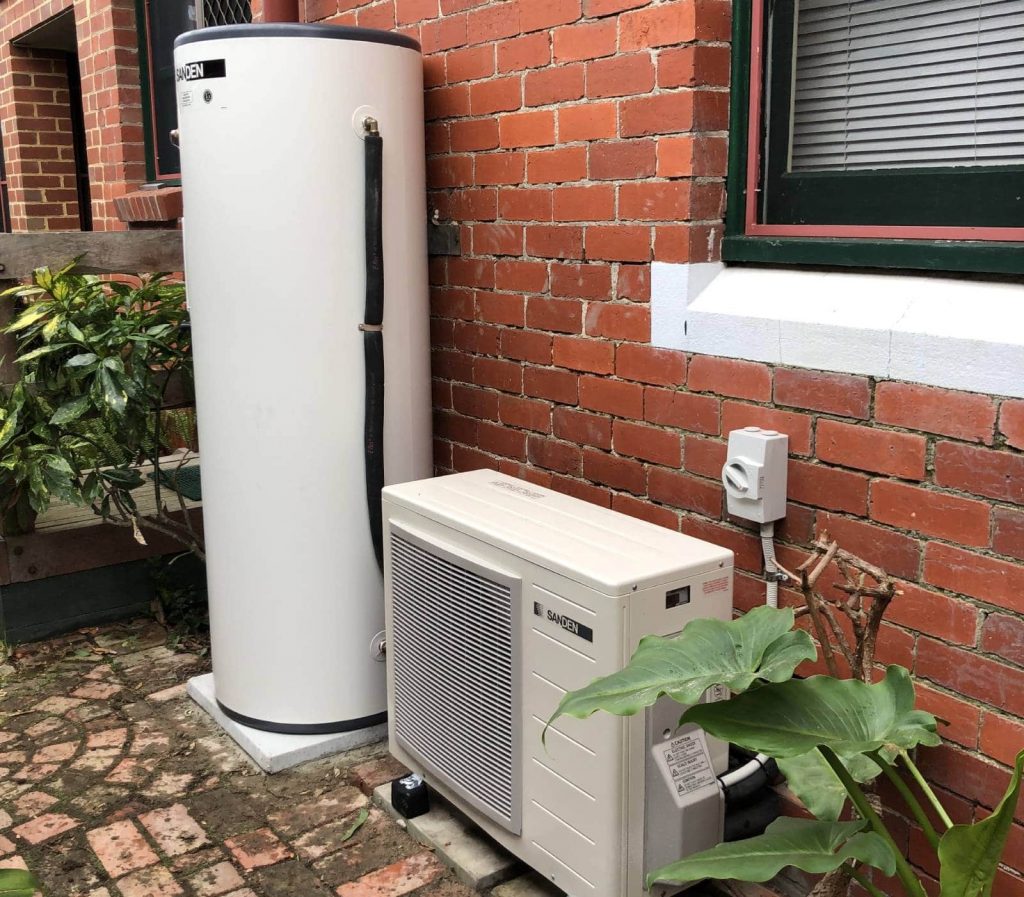

An interior coil acts as the evaporator and receives liquid refrigerant via a pump before being expanded.
The refrigerant absorbs the heat energy from the air that is blown across the radiators from within the house.
The generated chilly air is distributed via the ventilation system of the house. Since the liquid refrigerant absorbs the heat energy, it has become hot enough to evaporate into a gas.
Next, the gaseous refrigerant is compressed in a compressor. When gas is compressed, it generates heat. The system’s heated, pressurised refrigerant makes its way to the outdoor unit’s coil.
When the outdoor unit is in cooling mode, the condenser coils are exposed to air from the outside via a fan.
Due to the temperature difference between the inside of the house and the outside, heat is removed from the hot compressed nitrogen refrigerant in the coils and transferred to the cooler air outside.
As it cools, the refrigerant condenses and returns to a liquid condition. The expansion valves in the interior units receive the heated liquid refrigerant that has been pushed through the system.
As the tension of the hot liquid refrigerant is lowered by the expansion valve, the temperature of the refrigerant drops dramatically. The liquid refrigerant has cooled to the point where it can be reinjected to the indoor unit’s evaporator coil to start the cycle over again.
Installation Factors to Think About
Professional installation is required for air-source heat pumps. A local HVAC technician should be consulted for advice on equipment sizing, installation, and regular maintenance to maximise the effectiveness and dependability of your system. Soil testing may also be recommended in some cases to ensure optimal placement and stability of the outdoor unit.
Heat pumps typically require larger airflows to function effectively, so keep that in mind if you’re thinking about installing one to replace or complement your central heating system.
It’s possible that you’ll need to make adjustments to your ducting in order to accommodate the new heat pump without increasing the amount of noise or energy consumed by the fans. Consult with your contractor for advice tailored to your situation.
The price of installing an air-source heat pump in your home will vary based on factors such as the model you choose, the features you want, and the condition of your home’s current heating system and ductwork.
It’s possible that your new heat pump installation may need to be supported by adjustments to the ducting or electrical services.
Maintaining a Heat Pump
It is recommended that the filter be changed once a month if the heat pump is used often. If you just use the unit occasionally, you may be able to go three months before the filter needs to be replaced.
Keep the heat pump’s coils and blades clean, and have a professional inspect it twice a year, before the heating and cooling seasons.
The source of the issue should be pinpointed if at all possible. Is it only one register where airflow is weak, or do all of them? Is the annoying sound originating from the heat pump inside or the air ducts?
There are several items you may check for and try to fix on your own before calling a repairman, including the heat pump. When troubleshooting a non-functioning machine, the first step is to reset the motor.
Inspect the pump’s ignition system, and ensure there are no blown fuses or circuit breakers.
Make sure the thermostat is functioning properly by checking it out. If the filter is dusty, replace it, and ensure there are no obstructions to ventilation.
When the air ducts expand and contract, they can make a squeaking noise. To prevent this, you can try putting rubber cushions around them.
Loose components should be secured to prevent squeaks and rattles can be remedied by adjusting or replacing the fan belt that links the motor to the fan.
If the motor is making a grinding noise, it could be because the bearings are worn out and will need to be replaced by an expert.
Remember that if you aren’t mechanically minded, you generally shouldn’t try to conduct this repair job on your own.
Further supporting the idea that you should call in the pros is the fact that heat pumps may be home to potentially dangerous elements.
The release of harmful chemicals is terrible news, and a malfunctioning gadget poses serious risks to the user.
There is a 10 to 25 year lifespan range for a heat pump. The most crucial aspect of pump longevity is consistent inspection and maintenance. Those who reside in warmer climates tend to not only live longer but thrive.
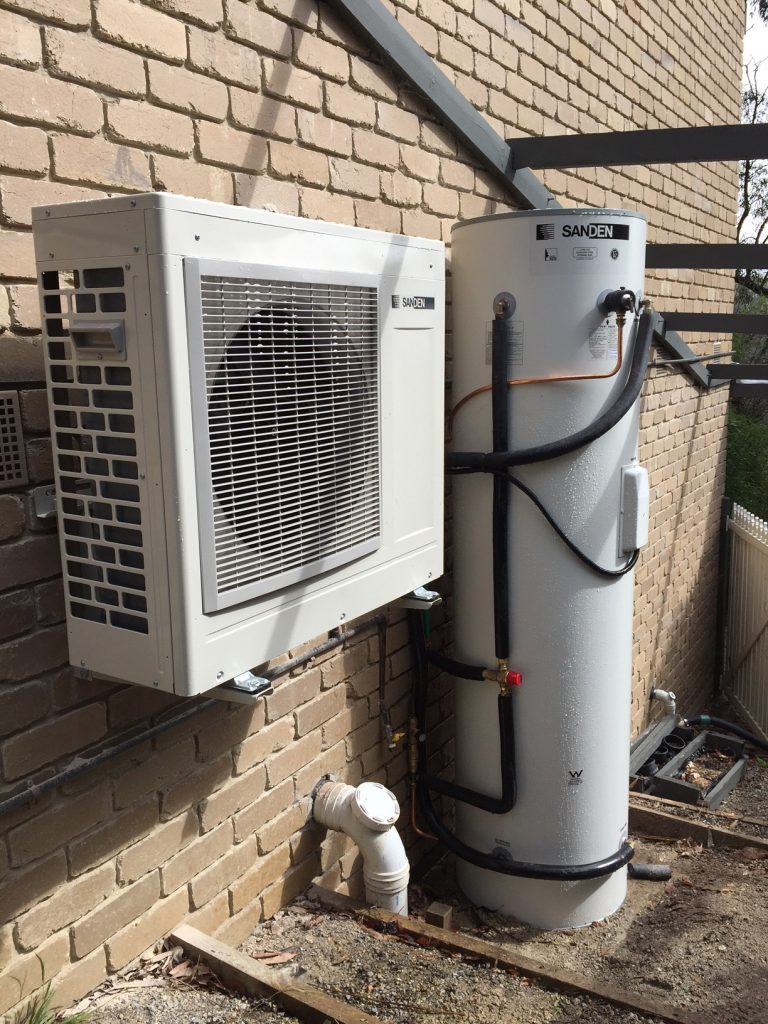

A heat pump may outlive a technician’s ability to service it if technological standards advance before the unit fails.
Keep a look out for new types of heat pumps as the new technology may make existing models safer or more energy efficient.
Consider installing a heat pump system in your home if you want to reduce the amount you spend on your monthly energy bill or maintain a consistent temperature in your home throughout the year. Machines known as heat pumps are able to transfer heat from one location to another.
Both the outside and the inner units contain components that are of equal value to the whole. The fluid known as a refrigerant is contained within the heat pump and is responsible for both absorbing and releasing heat. The temperature of the refrigerant and the pressure of the system both drop when the expansion valve is allowed to open.
The process of moving heat from one location to another using heat pumps involves bringing cooler air into contact with warmer air. The cost of having an air-source heat pump installed in your house will differ according to the type that you select and the features that you require. It is recommended that a local HVAC professional be approached for assistance on the proper sizing, installation, and maintenance of the equipment. To fit the new heat pump, it’s conceivable that you’ll need to make some modifications to the ducting in your home. If the filter has accumulated dust, you should replace it and make sure that there are no obstacles to the ventilation system.
If the motor is creating a grinding sound, it’s possible that the bearings have become worn out and need to be replaced. Always be on the lookout for new varieties of heat pumps because there is a possibility that they will be safer or more energy efficient.
